
Innovation doesn’t happen overnight—it follows a journey. The innovation lifecycle is the structured process that takes ideas from a spark of inspiration to real-world impact. It’s more than just brainstorming; it’s about moving through key stages such as ideation, validation, prototyping, iteration, and scaling. When organizations understand and embrace this lifecycle, they create a repeatable system for driving business growth, fostering creativity, and ensuring continuous improvement. By mastering these steps, you can turn raw concepts into transformative solutions that deliver lasting value for your customers and stakeholders.
The Five Stages of the Innovation Lifecycle
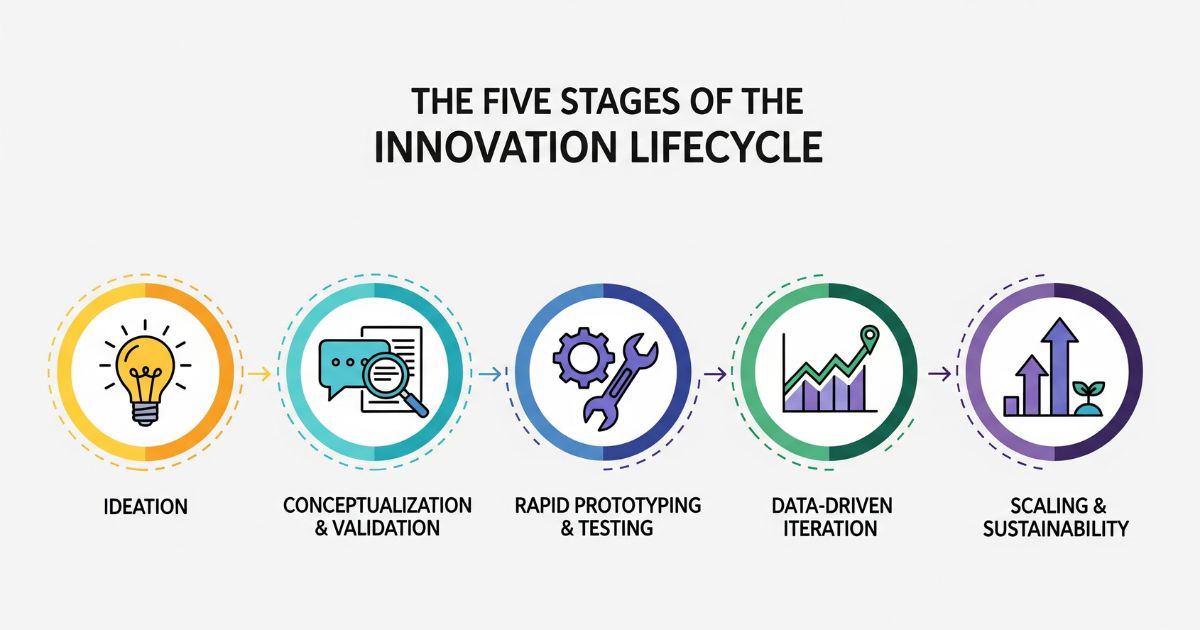
A robust innovation lifecycle comprises five sequential stages: Ideation, Conceptualization & Validation, Rapid Prototyping & Testing, Data-Driven Iteration, and Scaling & Sustainability. Each stage has distinct objectives, deliverables, and decision gates to ensure resources focus on the most promising opportunities.
Stage 1: Ideation
Ideation is the creative cradle where raw insights and inspiration collide. Start by gathering cross-functional teams—product managers, marketers, engineers, designers, and end-user advocates—to explore customer pain points, emerging trends, and technological enablers. Techniques such as design thinking workshops, mind mapping, and “How Might We” sessions help generate a diverse set of actionable ideas.
- Conduct empathy interviews to uncover unarticulated needs.
- Utilise trend forecasting and competitive analysis to identify market gaps.
- Host rapid ideation sprints with time-boxed brainstorming.
Aim to produce a backlog of 20–30 raw concepts, then score them against key criteria: customer impact, technical feasibility, strategic alignment, and ROI potential. The top 5–7 ideas move to the next stage.
Stage 2: Conceptualization & Validation
Not every idea survives real-world scrutiny. In the conceptualization phase, you refine your top ideas into clear value propositions and business concepts. Develop lean concept decks that outline problem statements, proposed solutions, target personas, channel strategy, and preliminary revenue models.
Validation is essential. Use low-cost experiments—surveys, landing-page tests, simple ad campaigns, or concierge MVPs—to gauge market interest. Measure engagement metrics such as click-through rates, sign-ups, and customer feedback. If interest falls below predetermined thresholds, pivot or deprioritize the concept.
Stage 3: Rapid Prototyping & Testing
Once a concept is validated, turn it into tangible prototypes. Leverage tools and platforms that support quick iterations—wireframing software, 3D printing, no-code app builders, or mockup kits. The goal is to create artifacts that stakeholders and end users can interact with, providing concrete feedback on usability, value, and desirability.
- Develop a low-fidelity prototype to test core functionality and user flows.
- Collect qualitative feedback through usability testing sessions.
- Iterate to a high-fidelity prototype, incorporating visual design and branding elements.
- Run A/B tests or pilot programs to compare variations and optimize features.
Document all insights and feature requests in a centralized product backlog. Regularly review feedback loops to decide whether to proceed, pivot, or halt development.
Stage 4: Data-Driven Iteration
Data is your most reliable compass. After launching a minimum viable product (MVP), instrument analytics to capture quantitative performance indicators: activation rates, retention curves, revenue per user, and customer support tickets. Correlate these metrics with qualitative feedback to prioritize enhancements.
Establish a cadence for iterative releases—weekly sprints or monthly feature drops. In each cycle:
- Analyze the previous release’s data against success criteria.
- Hypothesize improvements based on gaps and pain points.
- Design experiments or features to test those hypotheses.
- Deploy updates and measure impact, closing the feedback loop.
Stage 5: Scaling & Sustainability
A breakthrough idea becomes truly transformative when it scales effectively and sustainably. Prepare to expand by standardizing processes, optimizing operational workflows, and securing the right talent and resources. Key considerations include:
- Technical scalability: cloud infrastructure, microservices, and automation.
- Organizational readiness: clear roles, governance models, and cross-team alignment.
- Market expansion: localization strategies, channel partnerships, and go-to-market planning.
- Financial sustainability: predictable revenue streams, pricing optimization, and cost controls.
Embed continuous improvement by designating a “Scaling Task Force” that monitors key performance indicators and fosters best-practice sharing across product lines and geographies.
Building a Culture of Continuous Innovation
Even the best framework fails without a supportive culture. Encourage psychological safety so team members feel empowered to propose unconventional ideas. Recognize and reward experimentation, celebrate both big wins and instructive failures, and maintain transparent communication about priorities and lessons learned. Leadership must visibly champion innovation—allocating budget, setting clear metrics, and participating in ideation sessions.
Integrating Cross-Functional Collaboration
Breakthrough innovation often happens at the intersections of disciplines. Form dynamic squads that combine product owners, engineers, designers, data scientists, and marketers. Employ rituals like daily stand-ups, sprint demos, and “innovation jams” to keep momentum. Use collaborative platforms—digital whiteboards, shared backlogs, and integrated chat—to ensure real-time alignment and transparency.
Measuring Impact and Refining Strategy
Track both leading and lagging indicators to assess your innovation engine’s health. Leading metrics might include idea pipeline volume, prototype velocity, or pilot conversion rates. Lagging metrics encompass revenue growth, market share, customer lifetime value, and Net Promoter Scores. Review these metrics quarterly, recalibrate your roadmap, and reallocate resources toward the highest-impact initiatives.
Conclusion
Mastering the innovation lifecycle empowers organizations to translate bold ideas into tangible value consistently. By progressing deliberately through ideation, validation, prototyping, iteration, and scaling—and by nurturing a culture that celebrates creative risk-taking and encourages cross-disciplinary collaboration—you can build a sustainable engine for breakthrough growth. Start applying this framework today, and watch your ideas evolve from sparks of inspiration into market-defining realities.
Leave a Reply