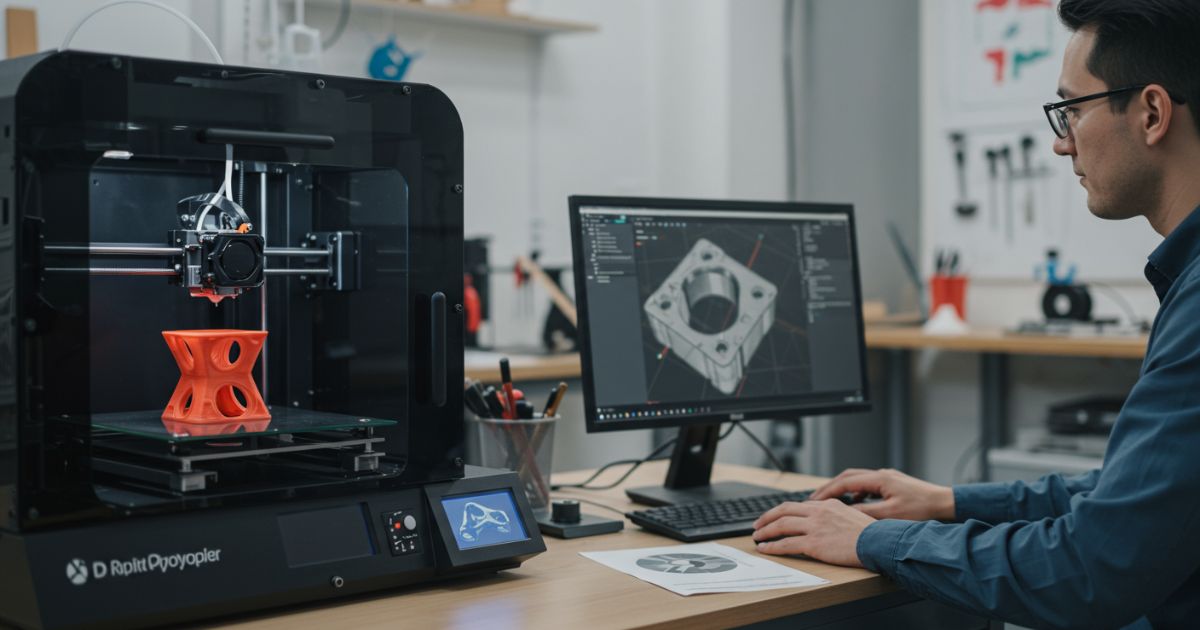

Innovation is the lifeblood of modern businesses, but taking an idea from an abstract concept to a market-ready product can be a complex, time-sensitive journey. Rapid prototyping is a proven approach that helps teams validate assumptions, gather user feedback early, and iterate quickly, reducing both time-to-market and development costs. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover a ten-step framework to streamline your innovation process. Whether you’re leading a startup or guiding a seasoned product team, these best practices will empower you to build prototypes that uncover real user needs and set the stage for successful product launches.
1. Define the Problem Precisely
Every successful prototype begins with a crystal-clear understanding of the problem you aim to solve. Conduct stakeholder interviews, market analysis, and competitive research to identify pain points and unmet needs. Frame the problem as a concise statement: “Busy professionals struggle to organize tasks across multiple platforms.” A well-defined problem statement focuses ideation sessions, helps prioritize features, and aligns your team around a common mission. Remember, if you prototype the wrong problem, no amount of iteration will yield a marketable solution.
2. Conduct User Research and Gather Insights
Deep user insights are the foundation of any prototype that resonates with real customers. Use qualitative methods—interviews, contextual inquiries, diary studies—and quantitative approaches like surveys or analytics reviews to map user behavior and expectations. Create user personas to distill common patterns and pain points. Document user journeys in flowcharts or storyboards to uncover friction points. This evidence-based approach ensures your prototypes address genuine user challenges rather than hypothetical scenarios, increasing the likelihood of product–market fit.
3. Brainstorm and Ideate with Cross-Functional Teams
Diverse perspectives fuel breakthrough ideas. Assemble cross-functional teams—designers, developers, marketers, subject-matter experts—and run structured ideation sessions. Techniques like mind mapping, SCAMPER, and Crazy 8s help generate a wide range of solutions. Encourage wild ideas before converging on feasible concepts. Use dot voting or impact-effort matrices to prioritize ideas that address the problem statement, align with business goals, and leverage your team’s strengths. Collaborative ideation lays the groundwork for prototypes that strike a balance between novelty and practicality.
4. Select the Most Promising Concepts
With a pool of potential solutions, it’s time to narrow your focus. Evaluate each concept against critical criteria—user desirability, technical feasibility, and economic viability. Create lightweight concept briefs outlining key features, value propositions, and risk factors. Conduct rapid sanity checks with stakeholders or a select group of target users to validate initial assumptions. By selecting one or two high-potential concepts, you streamline development and concentrate resources, setting the stage for impactful prototypes rather than scattered experiments.
5. Develop Low-Fidelity Prototypes
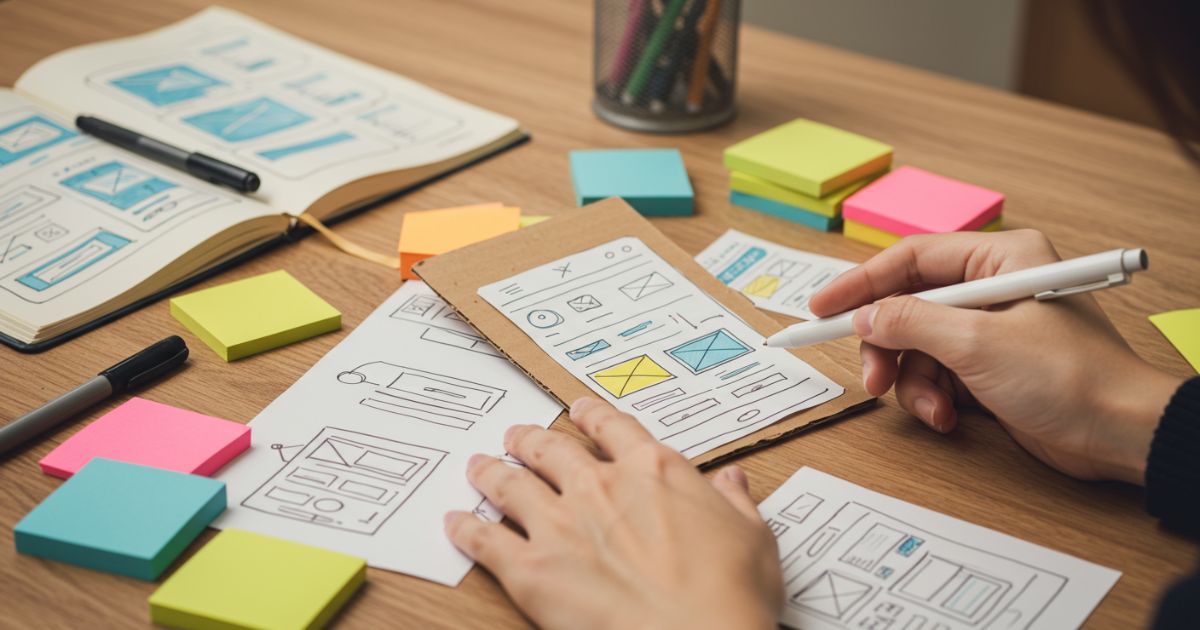

Low-fidelity prototypes—paper sketches, wireframes, or simple clickable mockups—enable rapid exploration of layout, flow, and fundamental interactions without heavy investment. Tools like paper and markers or digital platforms such as Balsamiq and Sketch let you visualize ideas in minutes. Conduct brief, informal walkthroughs with internal teams or a handful of users to spot glaring usability issues. The goal is to validate fundamental assumptions—navigation logic, information hierarchy, core feature set—before committing to detailed design and development.
6. Facilitate Iterative Testing and Feedback Loops
Iteration is at the heart of rapid prototyping. Schedule multiple short feedback cycles—ideally every one to two weeks—where you test the latest prototype with real users. Use moderated interviews or unmoderated testing platforms to collect both qualitative insights and quantitative metrics. Document feedback systematically, identify recurring themes, and adjust your prototype accordingly. This disciplined approach prevents feature bloat, uncovers hidden requirements, and keeps your project aligned with actual user needs throughout the development lifecycle.
7. Transition to High-Fidelity Prototypes
Once low-fidelity validation confirms your core concept, elevate your prototype’s fidelity. Design detailed UI mockups with realistic visual elements, typography, color schemes, and micro-interactions. Tools like Figma, Adobe XD, or InVision help you simulate near-production experiences. Integrate basic front-end code if needed to test performance or interactive features. High-fidelity prototypes help stakeholders and users better understand the final product vision and reveal subtle usability concerns that wireframes can’t capture.
8. Conduct In-Depth User Testing
High-fidelity prototypes open the door to rigorous user testing scenarios. Recruit a representative sample of target users and observe them completing real tasks—signing up, adding items to a cart, customizing settings. Record sessions to analyze pain points, error rates, and completion times. Complement qualitative observations with analytics data from prototype interactions. This dual approach ensures you uncover both surface-level and deep-rooted usability issues, refining your prototype until it meets predefined success metrics.
9. Decide, Pivot, or Persevere
With comprehensive user feedback and performance data in hand, evaluate your prototype against success criteria—user satisfaction scores, task completion rates, and business KPIs. If results meet or exceed targets, it’s time to move forward. If not, assess whether a pivot—changing a core feature or approach—could yield better outcomes. Sometimes, abandoning the prototype and returning to ideation is the bravest decision. Rigorous decision gates ensure you invest in ideas primed for market success rather than chasing illusions.
10. Plan the Path to Market and Scale
A validated prototype is only the beginning. Develop a detailed roadmap covering technical development, quality assurance, user onboarding, marketing strategies, and post-launch support. Define sprint plans, resource allocations, and go-to-market campaigns. Establish metrics for launch success and ongoing optimization, including activation rates, churn, and Net Promoter Score. By linking prototyping outcomes directly to execution plans, you close the loop from idea to market, ensuring a smooth transition from MVP to scalable product growth.
Conclusion
Rapid prototyping is more than a methodology—it’s a mindset of continuous learning and user-centered iteration. By following this ten-step framework, teams can de-risk innovation, accelerate time-to-market, and deliver products that truly resonate with customers. From defining the right problem to planning a robust go-to-market strategy, each phase contributes to a cohesive process that transforms ideas into impactful solutions. Embrace rapid prototyping, cultivate a culture of feedback, and watch your innovations move swiftly from concept to market success.
Visit Our Other Blog: Driving Breakthrough Innovation with Data-Driven Insights
Leave a Reply